Natural Compound Profiles
Catalog of botanical and natural compounds commonly explored for supporting joint flexibility and comfort
Each profile below offers purely educational information about natural ingredients. These descriptions explain the ingredient's origin, traditional uses, and general scientific understanding of its properties—without making specific health claims or product endorsements.
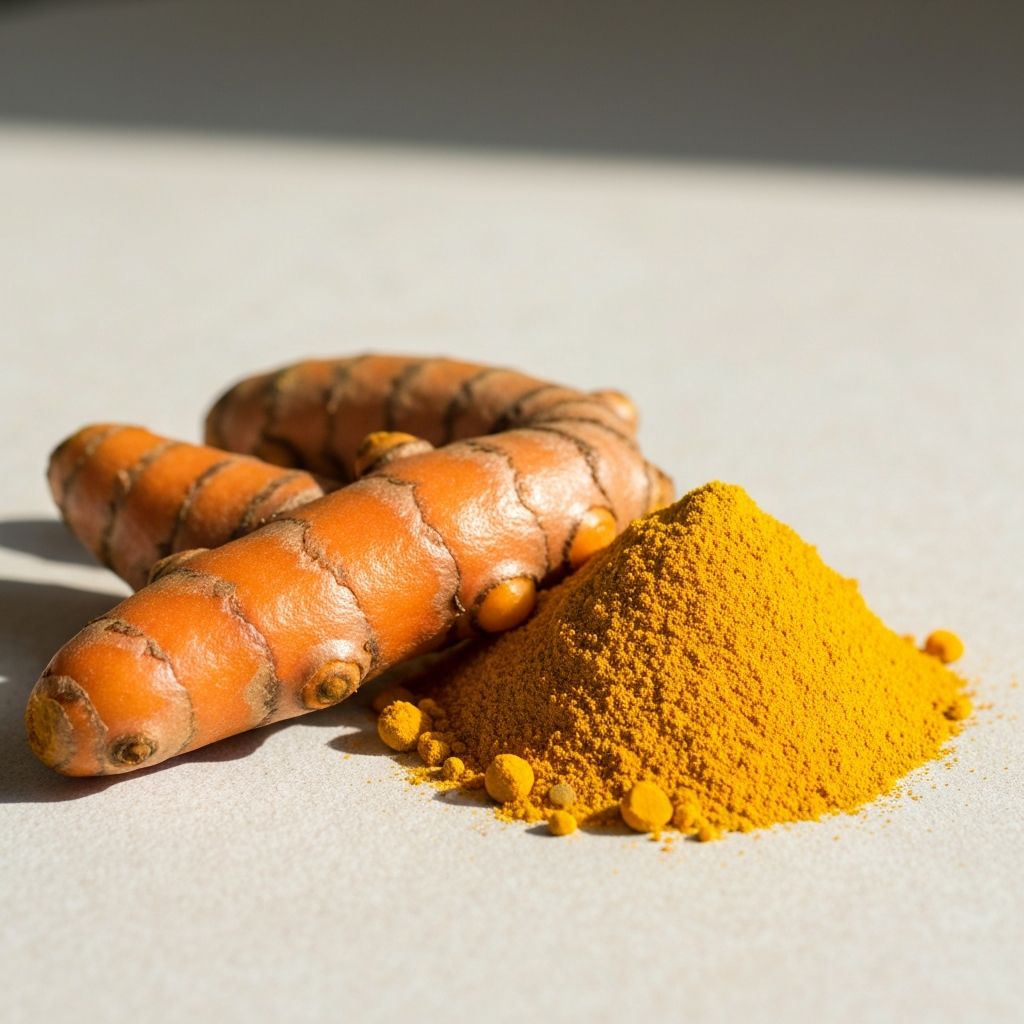

Turmeric (Curcuma longa) Extract
Turmeric is a vibrant golden spice derived from the root of Curcuma longa, a plant native to South Asia. For centuries, it has been used in traditional wellness practices and culinary traditions across various cultures.
The active compounds in turmeric, known as curcuminoids, are the focus of extensive scientific exploration. Research examines how these compounds interact with the body's natural systems to support overall physical comfort and well-being.
- Supports general well-being
- Used in traditional practices
- Contributes to a balanced diet
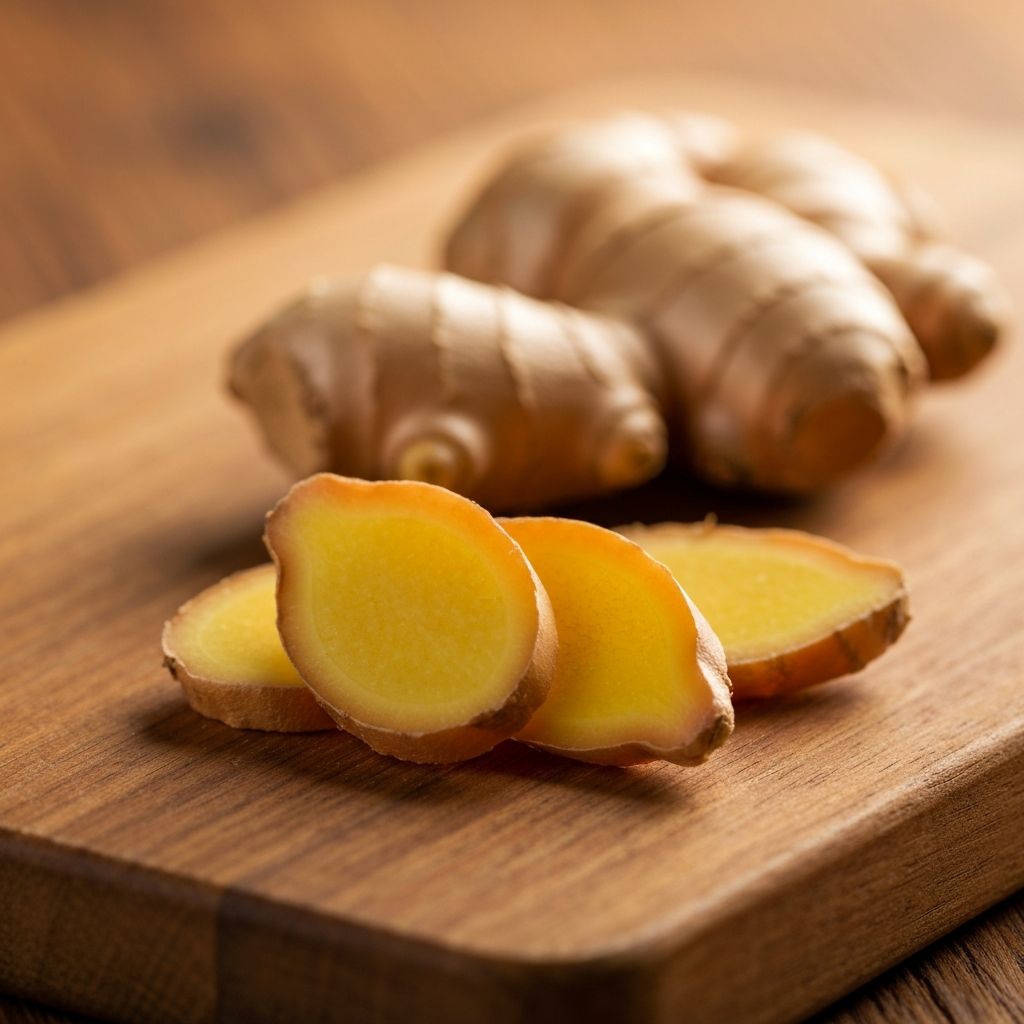

Ginger (Zingiber officinale) Root
Ginger is a widely recognized botanical known for its distinctive warm, peppery flavor and aromatic profile. The rhizome (underground stem) of Zingiber officinale has been valued in culinary and traditional wellness practices around the world.
The compounds within ginger, particularly gingerols and shogaols, are studied for their general contributions to bodily comfort and vitality. These compounds are considered part of ginger's broader profile of supporting an active, healthy lifestyle.
- Widely recognized botanical
- Supports digestive comfort
- Contributes to overall vitality

Glucosamine HCl
Glucosamine is a naturally occurring compound found in the human body, particularly in the cartilage and connective tissues that support joint structure and function. It can be derived from natural sources such as shellfish exoskeletons or produced through fermentation processes.
Glucosamine serves as a building block for cartilage matrix and is recognized for its role as a structural component. Understanding glucosamine's biological function helps clarify its place in discussions about joint health and mobility maintenance.
- Natural body compound
- Aids in tissue structure
- Supports joint flexibility
Chondroitin Sulfate
Chondroitin sulfate is a key component of cartilage, the connective tissue that covers the ends of bones in joints. It is a complex carbohydrate molecule that plays an important role in maintaining cartilage structure and resilience.
From an anatomical perspective, chondroitin sulfate contributes to the structural integrity and hydration of joint tissues. It helps cartilage retain water, which is essential for its shock-absorbing properties and overall joint function.
- Key cartilage component
- Supports tissue hydration
- Contributes to structural health

Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM)
MSM, or methylsulfonylmethane, is an organic sulfur-containing compound found naturally in various foods including garlic, onions, cruciferous vegetables, and meat. Sulfur is an essential element present in many bodily structures and compounds.
MSM serves as a natural source of bioavailable sulfur, which plays a role in various physiological processes, including the formation and maintenance of connective tissues. Understanding sulfur's biological functions helps contextualize MSM's place in supporting overall body structure and function.
- Natural sulfur source
- Supports connective tissues
- Found in many foods

Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a naturally occurring polysaccharide found throughout the body, with particularly high concentrations in synovial fluid—the lubricating fluid within joints. It is renowned for its remarkable ability to retain water, holding up to 1,000 times its weight in moisture.
As a natural lubricant and shock absorber, hyaluronic acid plays a critical role in maintaining joint cushioning and tissue hydration. Its presence in synovial fluid supports smooth joint movement and helps protect cartilage surfaces from wear and stress.
- Natural joint lubricant
- Supports tissue hydration
- Aids in joint cushioning
Learn More About Natural Compounds
Have questions or want to explore these topics further? We welcome your inquiries.
Reach Out to QuijexEducational content only. No promises of outcomes. All information presented is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice.